The prospect of communicating digitally with someone from beyond the grave is no longer a figment of scientific fantasy. Digital duplicates of the deceased have begun to turn quite some heads this year since Microsoft granted the patent for artificial intelligence technology that could bring dead people ‘back to life’ as chatbots. But while it seems like a significant and unexpected milestone in modern technology, one simply cannot overlook the ethical conundrum of this feat.
Most recently, freelance writer Joshua Barbeau is making headlines for virtually bringing his fiancée Jessica Pereira, ‘back from the dead’ eight years after she passed away. He paid Project December (a software that uses artificial intelligence technology to create hyper-realistic chatbots) five dollars for an account on their website and made a new text ‘bot’ named ‘Jessica Courtney Pereira.’ Next, he entered Pereira’s old Facebook and text messages, as well as offered some background information for the software. The resultant model was able to imitate his fiancée while chatting accurately.
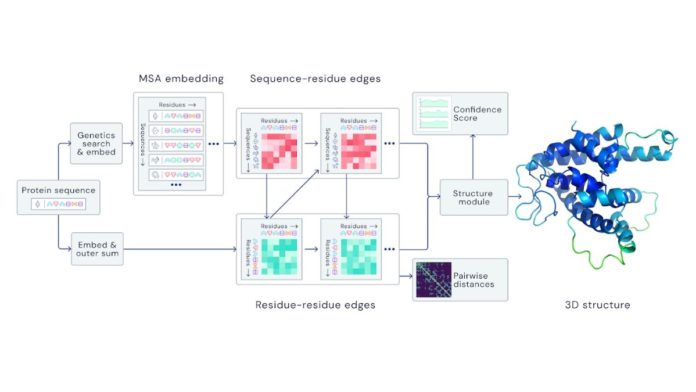
Project December is powered by GPT-3, an autoregressive language model that deploys deep learning to produce human-like text. It was developed by Elon Musk-backed research organization OpenAI. GPT-3 can replicate human writing by consuming a massive corpus of datasets of human-created text (particularly Reddit threads) and create everything from academic papers to emails.
The incident draws a parallel to the popular dystopian series Black Mirror and the movie Her. Without giving spoilers, in the episode “Be Right Back,” Martha, a young lady, grieves the death of her lover, Ash, who passed away in a vehicle accident. During Ash’s funeral, Martha learns about a digital service that will allow her to connect with a chatbot version of her late boyfriend and signs up for it later. In Her, the lonely protagonist dates Samantha, an intelligent operating system, with tormenting repercussions. The video depicts the psychological anguish that may befall on individuals who rely too much on technology.
Read More: Facebook Launched Its Open-Source Chatbot Blender Bot 2.0
In December 2020, Microsoft was awarded a patent by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) that outlines an algorithm technique for creating a talking chatbot of a specific individual using their social data. Instead of following the conventional method of training chatbots, this system would use images, voice data, social media posts, electronic messages, and handwritten letters to build a profile of a person.
According to Microsoft, “The specific person [who the artificchatbot represents] may correspond to a past or present entity (or a version thereof), such as a friend, a relative, an acquaintance, a celebrity, a fictional character, a historical figure, a random entity, etc.” The technology may potentially create a 2D or 3D replica of the individual.
In early 2021, South Korean national broadcaster SBS introduced a new cover of the 2002 ballad I Miss You by Kim Bum Soo, with folk-rock singer Kim Kwang-seok having performed the song. The twist here is, Kim Kwang-seok has been dead for nearly 25 years. According to the AI company Supertone, which reproduced the late singer’s voice, using voice AI system – Singing Voice Synthesis (SVS). This system had learned 20 songs of Kim based on a training tool with over 700 Korean songs to enhance accuracy so that the system can copy a new song in Kim’s style.
While all these innovations sound exciting and obviously creepy, it raises important questions on breaching privacy and possibility of misinformation. For instance, the Microsoft chatbot can be misused to put words on the mouth of the “dead person’s surrogate,” which they might have never said in real life, by using the crowd-sourced conversational social data to fill in the gaps.
It is also probable that such an artificial intelligence model may soon be able to “think” by itself. As a result, its subject person’s “digital existence continues to grow after the physical being has died away.” In this approach, the digital avatar of the deceased would stay current with events, form new ideas, and evolve into an entity based on a genuine person rather than a replica of who they were when they died.
In addition to that, the act of replicating someone’s voice also carries the risk of fraud, misinformation campaigns, and contributing to potentially fake news. Moreover, the artificial intelligence simulations of dead people could have a detrimental effect on real-world relationships. It can also worsen the grieving process if the users opt to live in denial due to having regular contact with the chatbot mimicking the dead.
The Kim Kwang-seok incident may have been well-received among the fans, but creating new works or resurrected voices using artificial intelligence poses copyright concerns. Who is the legal owner of the property? Is it the creator or team behind the AI software or the AI itself?
The new fad of reviving the dead is only getting started. In the coming years, humans will witness more believable performances of beloved dead relatives, artists, historical characters as technology advances. Unfortunately, they would not have any control over how their simulated avatar will be used. Therefore, such issues need to be addressed legally, ethically, and psychologically if artificial intelligence is to continue to be used in this direction.