DeepMind is a London-based artificial intelligence company owned by Alphabet, the parent company of Google. DeepMind was previously best recognized for developing a technology that could defeat the greatest human players in the strategic game Go, a landmark breakthrough in artificial intelligence. Recently, using DeepMind’s artificial intelligence, Sydney researcher Professor Geordie Williamson along with colleagues at Oxford started working on developing fundamentally new techniques in mathematics.
According to a recent study published in the journal Nature, the team of researchers from the universities of Sydney and Oxford has been working with DeepMind to apply machine learning to suggest new lines of investigation and to try to prove mathematical theorems. It is true that since the past few decades, computers have long been used to create data for experimental mathematics, but the challenge of detecting intriguing patterns has mostly rested on mathematicians’ intuition.
Now, with the help of machine learning, it is feasible to create far more data than any mathematician could possibly analyze in their lifetime. This is based on the premise that identifying data patterns in a machine learning dataset is analogous to finding patterns that connect complex mathematical objects by developing conjectures (assumption about how such patterns could work). If we can establish that these conjectures are correct, we can turn them into theorems.
Making a supposition from scratch is a far more difficult and subtle task. To refute a hypothesis, an AI just has to sift through a large number of inputs in search of a single case that contradicts the hypothesis. Developing a hypothesis or proving a theorem, on the other hand, needs insight, talent, and the linking together of several logical processes.
Professor Williamson leveraged DeepMind’s artificial intelligence to get close to proving a 40-year-old hypothesis about a representation theory, regarding Kazhdan-Lusztig polynomials. Known as the combinatorial invariance conjecture, it claims that there exists a relationship between certain directed graphs and polynomials. A directed graph is a set of vertices connected by edges, with each node having a direction associated with it. DeepMind was able to establish assurance in the existence of such a relationship using machine learning techniques, and hypothesize that it might be correlated to structures known as “broken dihedral intervals” and “external reflections.” Professor Williamson used this information to develop an algorithm that solved the combinatorial invariance conjecture. The new algorithm has been computationally tested across over 3 million cases.
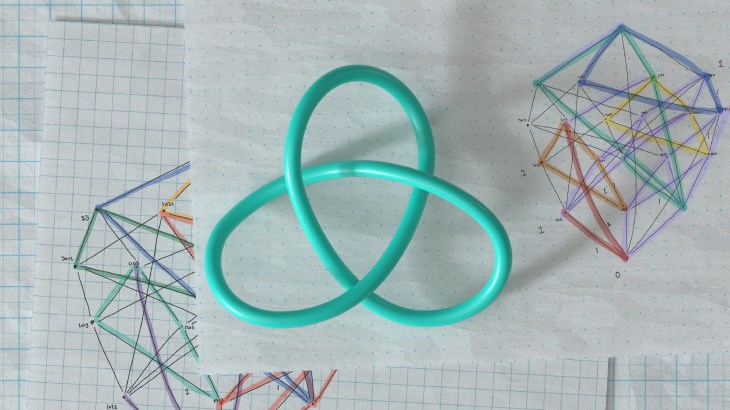
Meanwhile, University of Oxford co-authors Professor Marc Lackeby and Professor András Juhász established a startling relationship between algebraic and geometric invariants of knots, producing a whole new mathematical theorem.
As explained on the official blog of the University of Sydney, in knot theory, invariants are employed to solve the problem of differentiating knots from one another. They also help mathematicians in comprehending knot properties and their connections to other disciplines of mathematics. DeepMind also added that knots have connections with quantum field theory and non-Euclidean geometry.
Read More: DeepMind Trains AI Agent in a New Dynamic and Interactive XLand
The researchers next set out to determine which AI method would be most useful in identifying a pattern that connected two attributes. One approach, in particular, known as saliency maps, proved to be quite beneficial. It’s frequently used in computer vision to figure out which regions of an image contain the most important data. Saliency maps identified knot qualities that were likely connected to one another, and a formula was devised that appeared to be true in all situations that could be evaluated. Lackenby and Juhász then proved that the formula was applicable to a large class of knots.
While knot theory is fascinating in and of itself, it also has a wide range of applications in the physical sciences, including comprehending DNA strands, fluid dynamics, and the interaction of forces in the Sun’s corona.
“Any area of mathematics where sufficiently large data sets can be generated could benefit from this approach,” says Juhász. DeepMind believes that these techniques could even have applications in fields like biology or economics.