Recently, Terrain.art launched ‘Intertwined Intelligences,’ India’s first artificial intelligence non-fungible token (NFT) art exhibition, which showcases the relationship between artificial intelligence (AI) and human creativity. The exhibition is on display till August 20 and features six global artists pioneering AI — Pindar Van Arman, David Young, Scott Eaton, Harshit Agrawal, Sofia Crespo, and Feileacan McCormick from Entangled Others Studio.
Terrain.art is a blockchain-powered online platform that focuses on art from South Asia. Intertwined Intelligences, curated by Harshit Agrawal, is the initial phase in Terrain.art’s dedication to creating an environment for artists working in emerging kinds of art. This includes art forms like generative art, neural art, machine learning, and AI-assisted art, which intend to stimulate critical thinking about the kind of future the world of art should create using such technologies.
Harshit got into the limelight with his project “The Anatomy of Dr. Algorithm,” in which he fed photos of surgeries into an algorithm and employed artificial intelligence to produce Rembrandt-inspired art from images of everything from organs to fibroids. For the Terrain.art exhibition he curated 3000 landscape paintings and trained the computer to understand the visual patterns within them to generate its own set of landscape paintings.
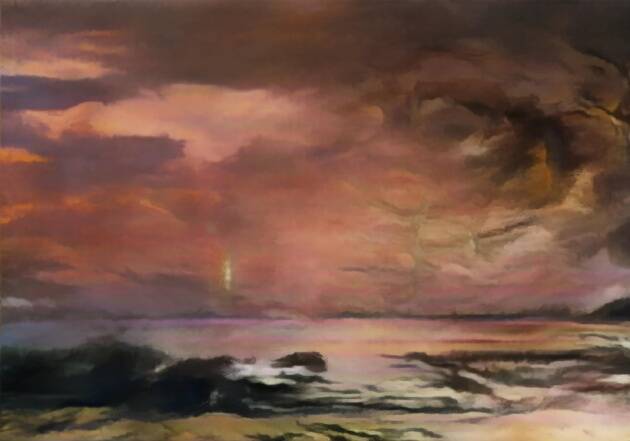

Latent Landscapes 4 by Harshit Agrawal (Source: PR Handout)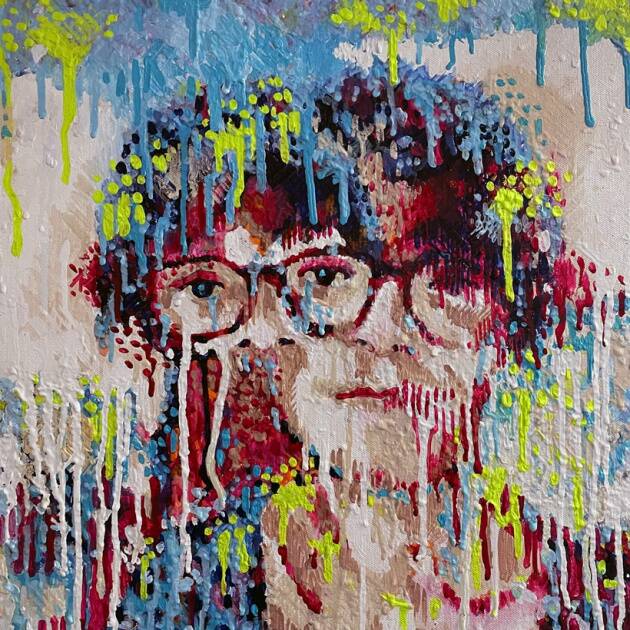 
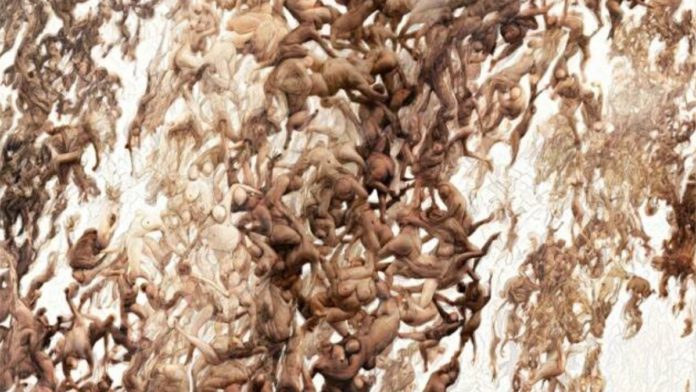
Sarah_15416 by Pindar Van Arman (Source: PR Handout) 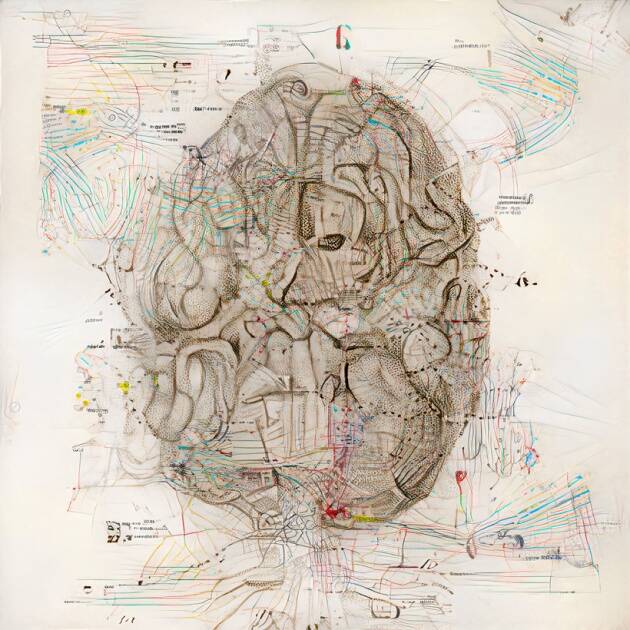
Tiny_Networks_of Everything by Sofia Crespo. (Source: PR Handout)
He explains that the artist can reconfigure their artwork by providing raw creative inputs into a GAN (generative adversarial network), a collection of machine learning algorithms that translate the artist’s inputs into visual media. The system has a lot of back-and-forths, but humans have the final word. Overall, encompassing this method, artificial intelligence offers artists a fresh set of frontiers to discover and cross.
This is not the first time India has hosted an exhibition of art influenced by artificial intelligence. Aparajita Jain, Founder of Terrain.art and Co-Director of Nature Morte, organized India’s first Al display, titled “Gradient Descent,” at Nature Morte in Delhi in August 2018, with all of the artworks created by Al in cooperation with artists. Today, Intertwined Intelligences on Terrain.art has added a new dimension by displaying works that have both physical and digital equivalents and are protected on blockchain using NFTs.
Aparajita says, “Human existence and digital technologies are no longer separable. Our lives are deeply intertwined within a web of technology, which itself is rapidly cultivating an intelligence of its own, seeded by human intelligence and mined data.”
The artwork on display includes 3D creatures that resemble living forms but were created using algorithms, as well as portraits painted by trained robots. This demonstrates how unlimited artistic ingenuity can be. Aparajita also predicts that gaming art will take over in the future when humans will be able to explore AI-generated augmented realities creatively.
Read More: IMD to leverage Artificial Intelligence for Better Weather Forecasting
The world of art is experiencing a quiet revolution, with Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs), allowing aesthetically talented artists to demand top pay for their work. Meanwhile, the combination of Covid-19 isolation and cryptocurrency earnings provided a strong motivation for digital-positive collectors to compete for these NFTs, and some creators are profiting handsomely. NFT also saves time and money spent in procuring or selling as well as prevents extra costs due to damaged artwork in the process. Additionally, since blockchain and cryptocurrencies operate in a decentralized marketplace, buyers of digital artwork and NFTs are largely unaffected by the traditional art and craft market.