By 2025, AMD hopes to achieve a 30x boost in energy efficiency in Artificial Intelligence (AI) training and High-Performance Computing (HPC) applications running on accelerated compute nodes using AMD EPYC CPUs and AMD Instinct accelerators. To achieve this audacious objective, AMD will have to enhance the energy efficiency of a computing node at a rate over 2.5 times faster than the industry’s overall progress over the previous five years.

Not only do we want to provide a better performance, but we also want to do it without using an excessive amount of power. In the next four years, AMD intends to increase the performance-per-watt efficiency of future server processors. However, AMD recognizes that this will be difficult because there isn’t much opportunity for process node energy efficiency improvements. As a result, the business will concentrate on improving its silicon architecture as the primary strategy for making its chips 30 times more efficient.

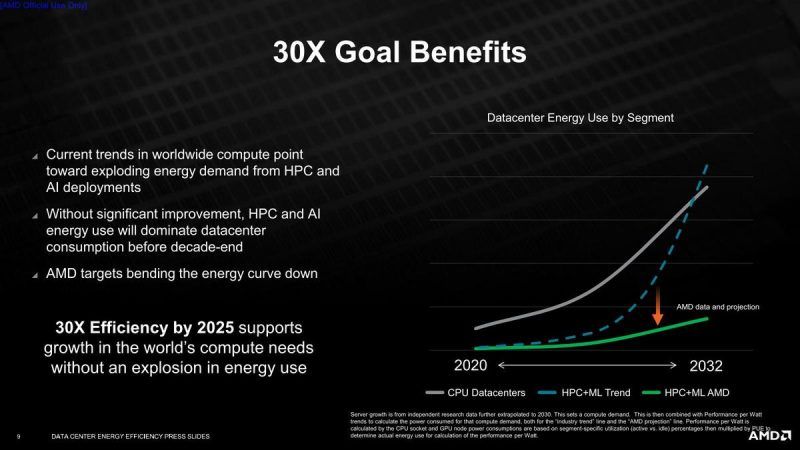
Accelerated compute nodes (ACNs) are the world’s most powerful and sophisticated computing devices, used for scientific research and large-scale supercomputer simulations. They offer scientists the computational power they need to make discoveries in various disciplines, including material sciences, climate prediction, genetics, drug development, and alternative energy. Accelerated nodes are also crucial for training AI neural networks, which are now leveraged for speech recognition, language translation, and expert recommendation systems with similar potential applications in the future decade. In 2025, the 30x objective would save billions of kilowatt-hours of electricity, lowering the power grid’s load.
According to AMD, if successful, it will reduce the power required for AI and HPC systems to complete a single calculation by 97% over five years.
AMD employs segment-specific data center Power Utilization Effectiveness (PUE) with equipment usage taken into consideration, in addition, to compute node performance/Watt metrics to make the objective particularly relevant to global energy use. The energy consumption baseline is based on the same industrial energy per operation improvement rates from 2015 to 2020, projected to 2025. To arrive at a relevant assessment of actual energy consumption improvement globally, the measure of energy per operation improvement in each segment from 2020-2025 is weighted by predicted global volumes multiplied by the Typical Energy Consumption (TEC) of each computing segment.
AMD has previously experimented with a slew of power-efficiency advancements in its CPU and GPU architectures, to the point where AMD’s Zen CPUs outperform Intel’s finest in terms of performance per watt.
According to speculations, AMD’s Zen 4 architecture will enable AVX-512, implying another way AMD can improve AI speed and efficiency. AMD has a lengthy history of supporting Intel extensions at n-1 extension sets or when the Intel extensions have been reserved for Intel devices for a long time.
Intel should have Sapphire Rapids with AMX (Advanced matriX Extensions) compatibility built-in by the time Zen 4 probably comes in late 2022 with reported AVX-512 support. By 2025, AMD may have implemented or been planning to add AMX support. It’s unclear how much efficiency AMD would gain by using these new SIMD processors.
AMD anticipates these improvements to significantly lower the rise in data center power usage, which is presently increasing exponentially, by 2032, such that if this objective is met, it will be virtually linear with a minimal slope.
Read More: Inside Intel’s Loihi 2 Neuromorphic Chip: The Upgrades and Promises
AMD also released its 26th annual Corporate Responsibility Report, which highlights the company’s achievements from the previous year, including success against its 2014 to 2020 targets, as well as additional goals for 2025 and 2030.
The company’s purpose-driven approach to high-performance computing is guided by four main environmental, social, and governance (ESG) strategic emphasis areas in this year’s report: digital impact, environmental stewardship, supply chain accountability, and diversity, belonging, and inclusion.


