Today, people use different coding languages for better results or just the zeal to learn something new. The history of coding languages is quite interesting and dates back to the early 1800s. Many modern coding languages have roots in Ada Lovelace’s first machine algorithm developed in 1843. Until now, nearly 9000 coding languages have been created, among which only the most popular ones that count to 150 are vastly used. Coders prefer some coding languages for a specific field like Python for developing websites and software, R programming for statistics, etc. With the development in technology, the coding languages are evolving too, which enhances the way of working, outputs, and the user experience. The translation of a code script or to translate coding languages is required when companies switch from one language to another, as Commonwealth bank of Australia did from COBOL to Java which cost them $750 million in five years. With AI’s application, transpilers are developed as coding languages translators to save money and time.
What is a coding languages translator?
A coding language translator is a tool that translates a program code from the source code into the destination code. Translating coding languages is like the same process of translating languages from one to another but complicated. In the process, we alter the data but want to preserve the data structure as far as possible. Theoretically, a piece of code is translatable to any other language if the programming languages are Turing complete. Turing completeness is a property in computability theory, where you can perform any computation on anything that any other computational method is capable of. We use compilers to perform translations on coding languages, but compilers are frequently used to change code so that a machine can interpret it. It requires a subset of compilers called transpilers for the code to be human-readable. Transpiler (aka source-to-source compiler) is a translator capable of translating between programming languages that operate on the same level of abstraction. Unfortunately, creating a transpiler in practice is challenging since different languages have different syntaxes and rely on various platform APIs and standard library functions.
Why it is difficult to translate coding languages?
Translation of coding languages is a tedious task that includes preserving the exact execution semantics and general code similarities at the same time. Besides, both the software you are working on and the languages to be translated makes the process challenging. When an application has many external dependencies that are difficult to replace in the target technology stack, the challenges are different than for an app that implements everything internally. You see, there can be several subtitles in either the source or the destination code, which need to be satisfying or may not matter in translation. Look at the ‘+’ operation in Python, C, and C#; the operand is the same operation yet performs differently. That is, mathematically, the addition is correct in Python but can expand more than 32 bits instead, it stays to 32bits only in C, and in C#, it may throw an exception depending on the mode. Another reason is the calling of library functions. When you translate programming languages with different semantics, for example, Python to C#, the Python functions in your code will not work in C# because they aren’t available in C#. Over time, many researchers came up with the idea of translating coding languages. Here is a list of tools for translating coding languages.
Read more: Top AI chatbot companies in India
List of coding languages translators
- Facebook’s TransCoder AI
TransCoder AI is a programming languages translator system developed by Facebook researchers, which can translate code among C++, Java, and Python languages. It is based on an unsupervised machine learning algorithm to perform translation and is one of the best Python transpilers. It was trained on over 2.8 million open-source projects and outperformed existing code translation systems using rule-based translation methods. TransCoder was first proposed in the paper, ‘Unsupervised Translation of Programming Languages, ‘ published on arXiv. The paper talks about transcompliers and how TransCoder works. The algorithm used in TransCoder is inspired by the neural machine translation (NMT) system to programming languages. The algorithm in TransCoder identifies common elements between input and output languages called tokens. Tokens can be defined as the keywords in programming languages like ‘for,’ ‘if,’ ‘else,’ ‘try,’ etc., and the mathematical digits and operators. Some tokens are the common strings that are present in the code. Then, the translation quality is improved by the algorithm using the back-translation method. The back-translation method induces to build source to destination code and destination to source code simultaneously and are coupled together at the end to give the final output. You can use the TransCoder by following the steps in the repository.
The testing for accuracy was done using 852 parallel functions in C++, Java, and Python from GeeksforGeeks. The computational accuracy was calculated while translating between C++, Java, and Python based on the BEAM seach of N=25, which is listed here.
Computational accuracy of translation between:
- C++ to Java – 74.8%
- C++ to Python – 67.2%
- Java to C++ – 91.6%
- Java to Python – 68.7%
- Python to Java – 56.1%
- Python to C++ – 57.8%
TransCoder works on a transformer-based sequence-to-sequence architecture consisting of an attention-based encoder and decoder. It follows three principles, one cross-lingual masked language model pretraining, denoising auto-encoding, and back-translation. Below is an illustration presented in the paper mentioned above.
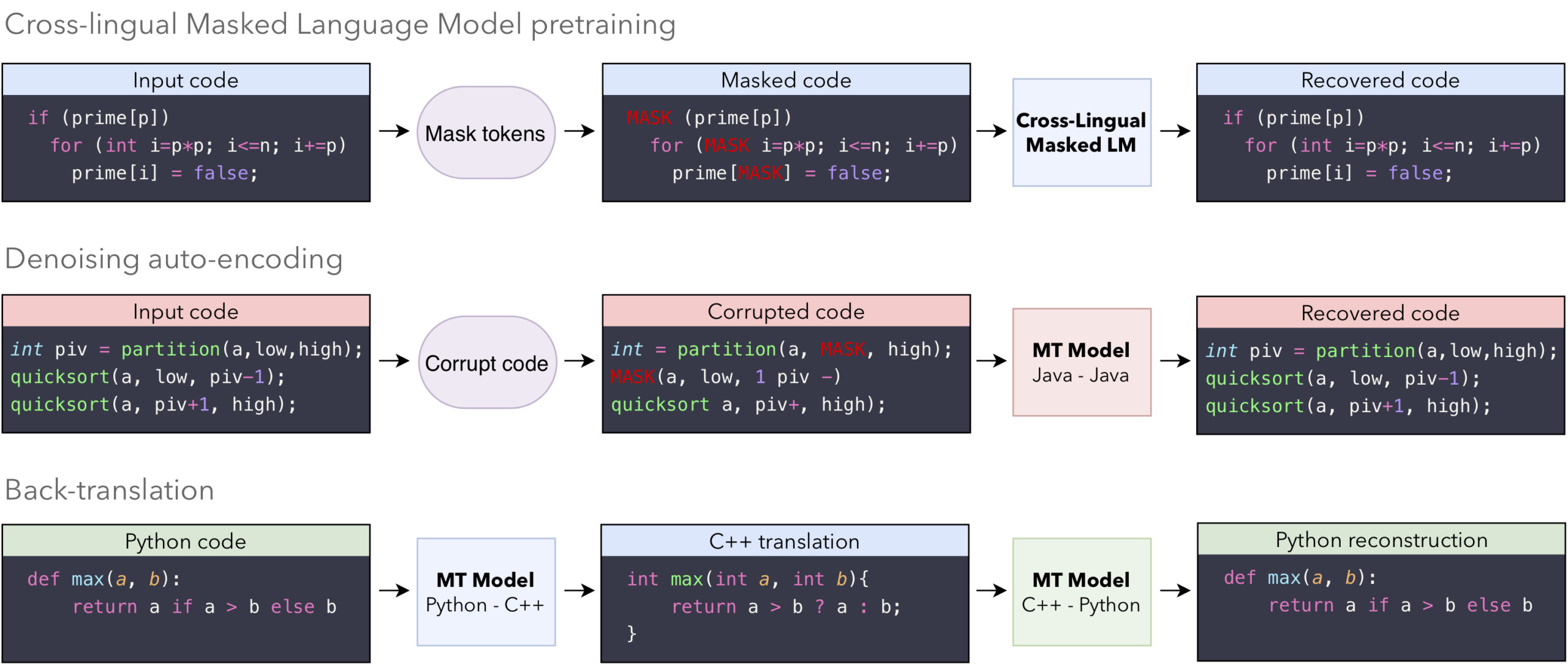 Source: arxiv.org
Source: arxiv.org
- IBM’s CodeNet
CodeNet is a work-in-progress project of IBM that has aimed to teach AI to code. At IBM’s Think 2021 conference, Arvind Krishna, CEO of IBM, revealed the project CodeNet, which is a two-year effort of Dr. Ruchir Puri and an IBM research team. The project CodeNet is a large-scale dataset with approximately 14 million code samples written in over 50 programming languages. The wide variety of languages and coding problems CodeNet has contains over a hundred solutions each for 80% of the problems. The idea behind project CodeNet is to enable researchers and developers to help in code search, code completion, code-to-code translation, and a combination of other use cases. A detailed description of project CodeNet is done in this paper, ‘CodeNet: A large-scale AI for code dataset for learning a diversity of coding tasks.‘ CodeNet is similar to ImageNet, a computer vision dataset having 14 million images scattered across 20,000 categories. Though the operation of CodeNet to translate code-to-code is not ready yet, it is a promising project and expects to perform well.
Read more: Whisper: Openai’s Latest Bet On Multilingual Automatic Speech Recognition
- Google’s GWT
GWT, Google web toolkit, is a development toolkit for building and optimizing complex browser-based applications. It is an open-source set of tools allowing developers to create and maintain JavaScrip front-end applications. GWT’s objective is to make it possible to construct high-performance web apps productively without the developer having to be an expert in JavaScript, XMLHttpRequest, or browser quirks. GWT is a popular coding languages translators that work to create and debug AJAX apps in Java, and when pushed to production, the compiler converts your Java application to browser-friendly JavaScript and HTML.
GWT has two major components:
- GWT SDK: It contains the Java API libraries, compiler, and development server. It allows the user to write client-side applications in Java and deploy them as JavaScript.
- Plugin for Eclipse: It provides IDE support for GWT and app engine web projects.
You can start using GWT. The first step is to download the SDK and take in-depth tutorials to understand the fundamentals of GWT development.
- GitHub Copilot
GitHub Copilot is an AI pair programmer powered by OpenAI Codex, a new AI system created by OpenAI. It helps developers to write code faster with fewer efforts by offering autocomplete-style suggestions as you code. The suggestions are given either while writing the code directly or by writing a natural language comment about what you want the code to do. It is similar to giving commands to write code. GitHub Copilot provides various use cases with coding, including writing code with a simple command in more than one language, creating dictionaries of lookup data, navigating a new codebase with GitHub Copilot Labs, and more.
The GitHub Copilot Labs is a companion extension to GitHub Copilot, which can be installed from the visual studio marketplace. It is a visual studio code extension that contains experimental applications of Copilot, which are ML-powered editor features for developers. One of the features of Copilot Labs is translating coding languages from one to another, which comprises around 60 coding languages to choose from.
The process of coding translation consists of only three steps:
- Install the GitHub Copilot Labs extension.
- After installing Copilot Labs, open the folder you want to translate, then click on the extension icon.
- Now, you can see the window ‘Translate code into:’, highlight the code, select your desired language and click on ‘Ask Copilot’.
Following the steps mentioned above, your code will be successfully translated.
The task of code language translation is challenging, and many will find it amusing to become a reality. We have just a handful of coding languages translators, but we are hopeful and believe the best is yet to come. For now, Facebook’s TransCoder shows remarkable results, successfully understanding the syntax specific to each language and learns data structures and their methods. At higher levels, maintaining a transpiler is more difficult than developing one as new technologies emerge and new features are introduced when programming languages advance. As a result, the work on transpilers is a consistent process and will need more hands on the deck.