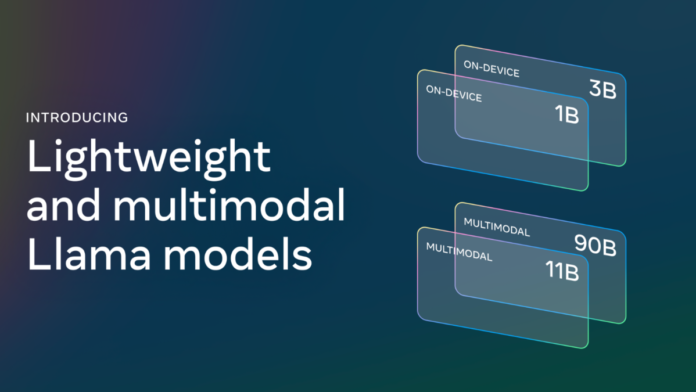
Meta released Llama 3.2 on September 25, 2024, two months after Llama 3.1 launch. This new version includes both vision and text models which are tailored to enhance various applications from image understanding to summarizing tasks.
Llama 3.2 vision models 11B and 90B are designed for image reasoning tasks like document-level understanding, including charts and graphs, captioning, and visual analysis. These models bridge the gap between vision and language by extracting specific details from an image, understanding it, and then generating an answer. You can use Llama 3.2 11B and 90B for custom applications using Torchtune, deploy them locally using Torchchat, and also connect through the smart assistant Meta AI.
The lightweight models of Llama 3.2, 1B, and 3B support context lengths of 128k tokens and are utilized for tasks like summarization, rewriting tasks on edge, or instruction following. Meta uses two methods for these models: pruning and distillation, which makes them highly lightweight and able to fit on devices efficiently.
These models can also run locally, ensuring privacy and instantaneous responses, as the data does not need to be sent to the cloud for processing. This makes Llama 3.2 1B and 3B ideal for applications requiring strong privacy protection.
Read More: Meta Launches AI-Driven Assistant: Metamate
In conjunction with the model release, Meta is also offering a short course on Llama 3.2, taught by Amit Sangani, Director of AI Partner Engineering at Meta. The course deep dives into the capabilities of Llama 3.2. You can find the course on DeepLearning.AI, an online education platform that released the course in partnership with Meta. Here’s what you can learn from it:
- Features of Meta’s four new models and when to use which Llama 3.2 model.
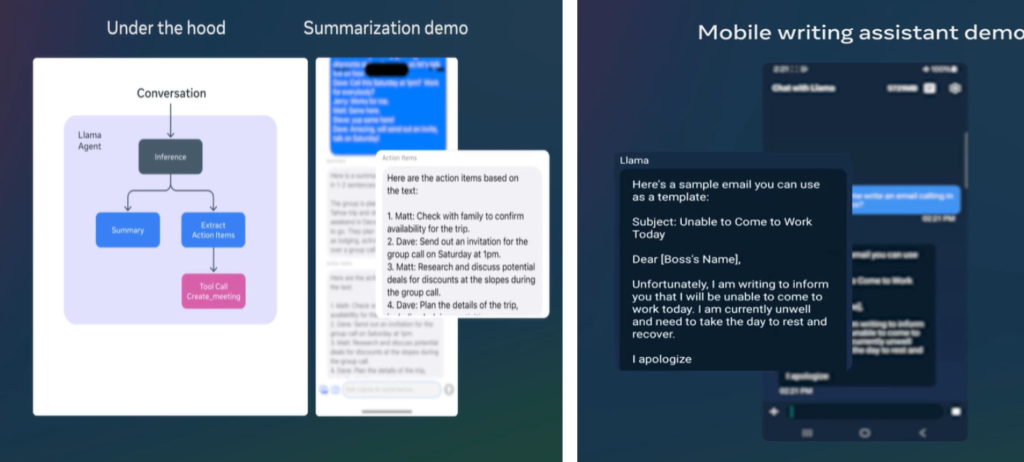
- Best practices for multimodel promoting and application to advance the image reasoning with many examples.
- Know the different user roles used in Llama 3.1 and 3.2, including system, user, assistant, and ipython, and the prompts used to identify these roles.
- Understand how Llama uses the Tiktoken tokenizer and how it expands the vocabulary size to 128k to improve encoding and multilingual support.
- Learn about Llama Stack, a standardized interface for toolchain components like fine-tuning and synthetic data generation that is useful for building agentic applications.
This launch demonstrates Meta’s commitment to open access and responsible innovation. By offering the short course, Meta ensures that developers can access the necessary tools and resources to build applications.