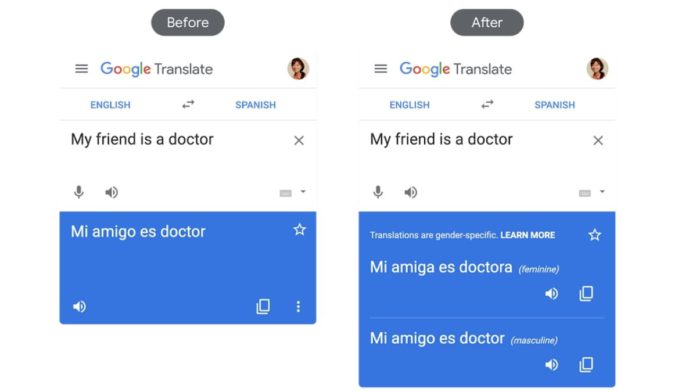
Google AI announced the development of a new dataset to curb gender bias in machine translation. The dataset was developed by picking up contexts from surrounding sentences or passages.
Although Neural Machine Translations (NMT) advances paved the way for natural and smooth translation, the gender stereotype is due to the data they were trained on. As the conventional NMT methods translate sentences individually and do not include gender information explicitly, the bias is being observed.
To overcome the bias, Google AI will be using Translated Wikipedia Biographies dataset to evaluate training models. “Our intent with this release is to support long-term improvements on ML systems focused on pronouns and gender in translation by providing a benchmark in which translation accuracy can be measured pre and post-model changes,” mentioned Google AI in a blog post.
Read more: Measuring Weirdness In AI-Based Language-Translations
The dataset was developed by picking up a group of instances with identical representation across the globe and genders. These were extracted from biographies on Wikipedia based on occupation, profession, and activity. For an unbiased selection, occupations were chosen in such a way that they were gender associated. To overcome the geography-based bias, all the instances were divided based on geographical diversity. The dataset is diverse, with entries from individuals from more than 90 countries across the world.
The new dataset opens a new basis of evaluation for gender bias reduction in machine translations by referring to a subject with known gender. This computation is flexible in English translation since English pronouns are profoundly gender-specific. This computation method has resulted in a 67% reduction in errors on context-aware models versus previous models.