Data management is critical to modern businesses. It enhances operations’ overall efficiency and drives growth. By implementing the proper data management strategies, you can ensure data availability, integrity, and compliance across your organization.
Enterprise data management (EDM) is a comprehensive process that assists you in managing data strategically. It ensures data is available, consistent, and protected to meet organizational goals and facilitate business continuity.
This article provides an overview of enterprise data management (EDM) and why it is essential for your business. You will also learn how to implement a robust EDM strategy for effective data management.
What is Enterprise Data Management?

Enterprise data management is a systematic approach to managing and governing data. It helps to create assurance and confidence in an organization’s data assets.
EDM involves establishing policies and procedures to ensure data accessibility, consistency, accuracy, security, and compliance with industry standards. It enables you to consolidate data from various sources and store it in a standardized and accessible format to optimize business operations.
Why Is Managing Enterprise Data Critical to Business?
Managing enterprise data is critical to business for several reasons:
Informed Decision-Making
When the data is accurate, you can make informed decisions based on factual figures rather than intuition. Enterprise data management practices ensure your data is correct by allowing you to identify inconsistencies or errors within the data. You can take preventive measures to clean and transform it. This way, your team can identify high-performing products and adjust marketing strategies.
Operational Efficiency
Within the enterprise data management framework, you can define policies and procedures that help maintain data consistency across the organization. Standardizing data across different systems and departments enables you to enhance operational efficiency and improve data accessibility and collaboration.
Customer Insights
EDM allows you to consolidate data from multiple sources, such as marketing platforms, social media, CRM systems, and more, in one place. It helps you gain a comprehensive view of customer data. By analyzing this information, you can identify areas of improvement and enhance customer satisfaction by addressing their concerns about your products and services.
Compliance and Risk Management
Enterprise data management helps you know what regulations to comply with to mitigate data security risks. You can establish protocols for monitoring data usage and access controls, protecting data from unauthorized access, and complying with regulatory standards. The security measures reduce the risk of invasion, compliance penalty risk, and reputational damage.
How to Implement Enterprise Data Management Strategy
Implementing a robust enterprise data management strategy includes several factors. Here is a detailed guide to the factors involved in creating a data management framework for your organization:
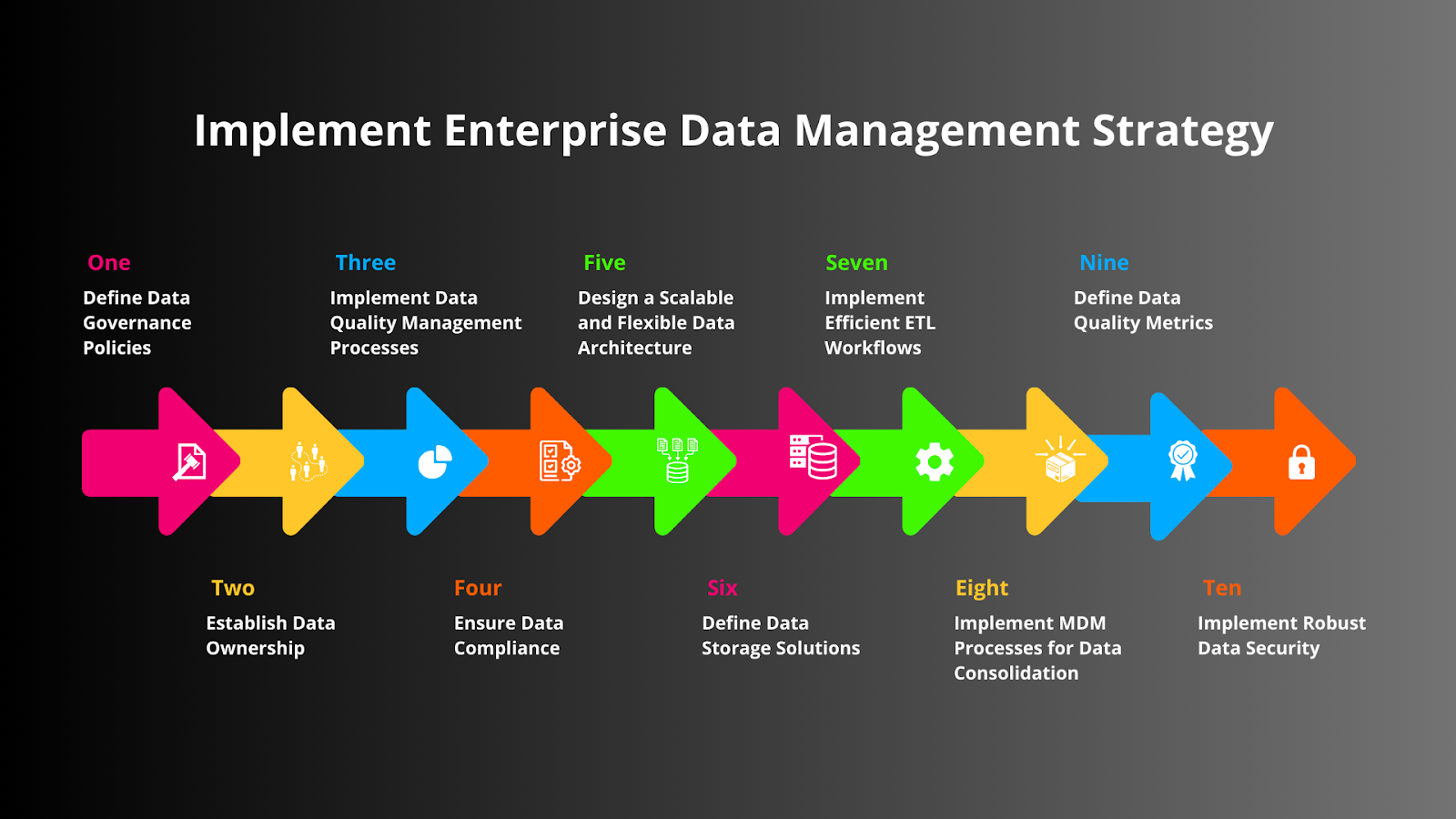
Define Data Governance Policies
Data governance policies are a set of regulations, procedures, and guidelines that define how to manage, access, and use data. These regulations include policies for data classification, access permission, quality standards, compliance, integration, security, and retention. You must define all the necessary policies to conduct your business operations efficiently.
Establish Data Ownership
When you establish data ownership, you define the roles and responsibilities of individuals accountable for managing and protecting specific datasets. Clearly define the authority of the data owners to ensure data quality and integrity.
Implement Data Quality Management Processes
Data quality is essential for making accurate and informed decisions. Implementing a data quality management process includes activities like data cleaning, validation, and enrichment, which help identify errors, inconsistencies, and duplicate data.
Ensure Data Compliance
Data compliance is essential to protecting your organization’s critical data assets, mitigating risks related to legal obligations, and ensuring data credibility. Identify the relevant regulatory compliance specific to your industry to conduct regular audits and comply with regulatory obligations such as HIPAA, GDPR, PCI DSS, etc.
Design a Scalable and Flexible Data Architecture
A well-designed data architecture allows you to scale data and be flexible with data management, enhancing your business’s operational efficiency. A sturdy data architecture must have the following capabilities:
- Smooth data integration
- Scalable data storage
- Efficient data processing
- Data Analytics
Define Data Storage Solutions
You must analyze your organization’s requirements before choosing a data storage solution to implement an enterprise data management framework. Some of the specifications can include:
- The type of database, relational or non-relational
- Scalability
- Data compression for storage efficiency
- Data indexing and partitioning are needed for better data accessibility.
Implement Efficient ETL Workflows
ETL workflows use integration tools, such as Airbyte, to extract data from different sources, transform it, and load it into the target system for further analysis. By implementing the ELT process, you can automate your workflows and increase data performance and reliability.
Implement MDM Processes for Data Consolidation
Master data management (MDM) is a process for centralizing and governing critical organization data. By establishing data governance controls and quality rules within the MDM environment, you can ensure consistency and synchronize master data across your organization.
Define Data Quality Metrics
Data quality measures are essential for managing enterprise data with consistency and timeliness. Within the quality measures, you must define the metrics and KPIs to help you evaluate data quality across the organization.
Implement Robust Data Security
Nowadays, data security is the most critical concern for organizations. A comprehensive data security strategy should include encryption methods, access controls, and authentication mechanisms. By implementing data security, you can conduct regular assessments to detect and prevent intrusion and allow role-based access to protect sensitive information.
Master Data Management Vs. Enterprise Data Management
Enterprise and master data management are related but have distinct scopes and functions. EDM is a broader concept that covers the entire lifecycle of your data across the organization. In contrast, MDM focuses on managing the master data (critical data entities within the business environment). Let’s look at some of the essential differences between MDM and EDM.
| Basis of Difference | Master Data Management (MDM) | Enterprise Data Management (EDM) |
| Definition | It is the process of creating uniform data related to a single entity, such as a product, customer, or supplier, across different departments. | It is managing, storing, and governing data within an organization. |
| Purpose | To make data more consistent for operational and analytics use. | To oversee the entire data lifecycle and ensure effective data management and governance. |
| Scope | Limited for managing and maintaining the master data. | It has various attributes and manages all the data within the organization, including the data types and sources. |
| Functionality | MDM centralizes the management of crucial data entities of your business by integrating in one place and synchronizing the workflows | There are many aspects of EDM, including data management, governance, quality management, integration, security, architecture, and compliance |
| Example | A retail company can use MDM to create a single view of customer data, including interactions with products, website visits, products bought, and feedback. This will help the company better understand the customer and create targeted campaigns to improve performance efficiency. | A finance company can implement EDM to govern data from various sources, including payment gateways, account information, and daily transactions. This helps identify unusual activity and optimize investment strategies to provide a personalized customer experience. |
Few Enterprise Data Management Tools
Enterprise data management tools are vital in establishing, monitoring, and optimizing organizational data practices. These tools facilitate data quality management, ensuring the data is accurate, complete, and consistent for developing and implementing strategic business decisions.
Let’s look at some of the enterprise data management tools:
- Tableau: Tableau is a data visualization tool that simplifies raw data and helps you present it in an understandable format. It allows you to create interactive dashboards and reports, providing a clear view of your enterprise data and resources.
- Dell Boomi: This enterprise-grade platform is designed to provide high productivity by enabling you to synchronize data within a centralized hub. It lets you connect various systems and applications to streamline data flow, ensuring the information is updated across the organization.
- SAP Master Data Governance: This tool focuses on managing the master data entities within your organization. It integrates with both SAP and non-SAP systems. SAP Master Data Governance gives you a unified view of your data and helps you meet industry standards for better compliance.
- IBM InfoSphere QualityStage: This data management tool specializes in quality management through data profiling, cleaning, and standardization. It helps you identify duplicate values and reduce redundancy, enhancing data quality.
Key Takeaways
Enterprise data management (EDM) is a strategic practice that helps you manage your enterprise data through data quality, governance, and security measures. By implementing EDM, you can make informed decisions, foster a data-driven culture, mitigate risks related to security and compliance, and increase operational efficiency. You can also use third-party tools to apply EDM to streamline workflows within your organization.
FAQs
What are the examples of enterprise data?
Examples of enterprise data include:
- Operational data, such as transactions, inventory levels, customer orders, accounting, and HR statistics.
- Strategic data that includes reports, CRM platform data, market trends, and opportunity analysis.
- Application-specific data like GPS for transportation.
- Network alerts for maintaining IT infrastructure.
What is the EDM framework?
An enterprise data management framework is a set of practices implemented within your organization’s environment to manage the data effectively.
Which team is responsible for EDM?
The enterprise data managers, including database and IT administrators or project managers, manage enterprise data.


